16 Dec, 2022
With the completion of the payload check outs and the previously completed orbital control maneuver, ispace has now achieved the first four milestones of its Mission 1 milestones. Milestone 4 was completed at 12:00 on Dec. 15, 2022 (Japan Standard Time) and subsequently announced.
The HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lander, which was successfully launched by a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 2:38 a.m., Saturday, December 11, 2022 (U.S. Eastern Time), carries 7 payloads. The upper part of the lander is designed to accommodate customer payloads including experimental equipment and multiple lunar rovers. This area is designed to protect payloads from the harsh environment of space and is maintained at a constant temperature range, allowing various activities to be carried out, depending on customer needs. The lander provides power and communication with Earth, making it possible to carry out these research and development activities—from the time of lander startup, until the end of operations.
After a steady operational state of the lander was established, customer payloads were checked out individually. ispace confirmed the temperature, attitude, power supply, and communications connectivity of each customer payload, and confirmed that the lander is capable of operating the payloads as planned. As of today, all confirmation processes have been completed.
After completing the first orbital control maneuver, the lander continues to maintain a stable attitude and power supply. The next phase of the mission involves nominal cruise and further orbital control maneuvers to be conducted during a 1-month cruise period. Once this period elapses, the Mission 5 milestone success will be achieved, and an announcement made.
(Update) Camera Position
A previously released image in the December 14 press release misidentified the location of a camera on the side of the lander. The image below updates that information.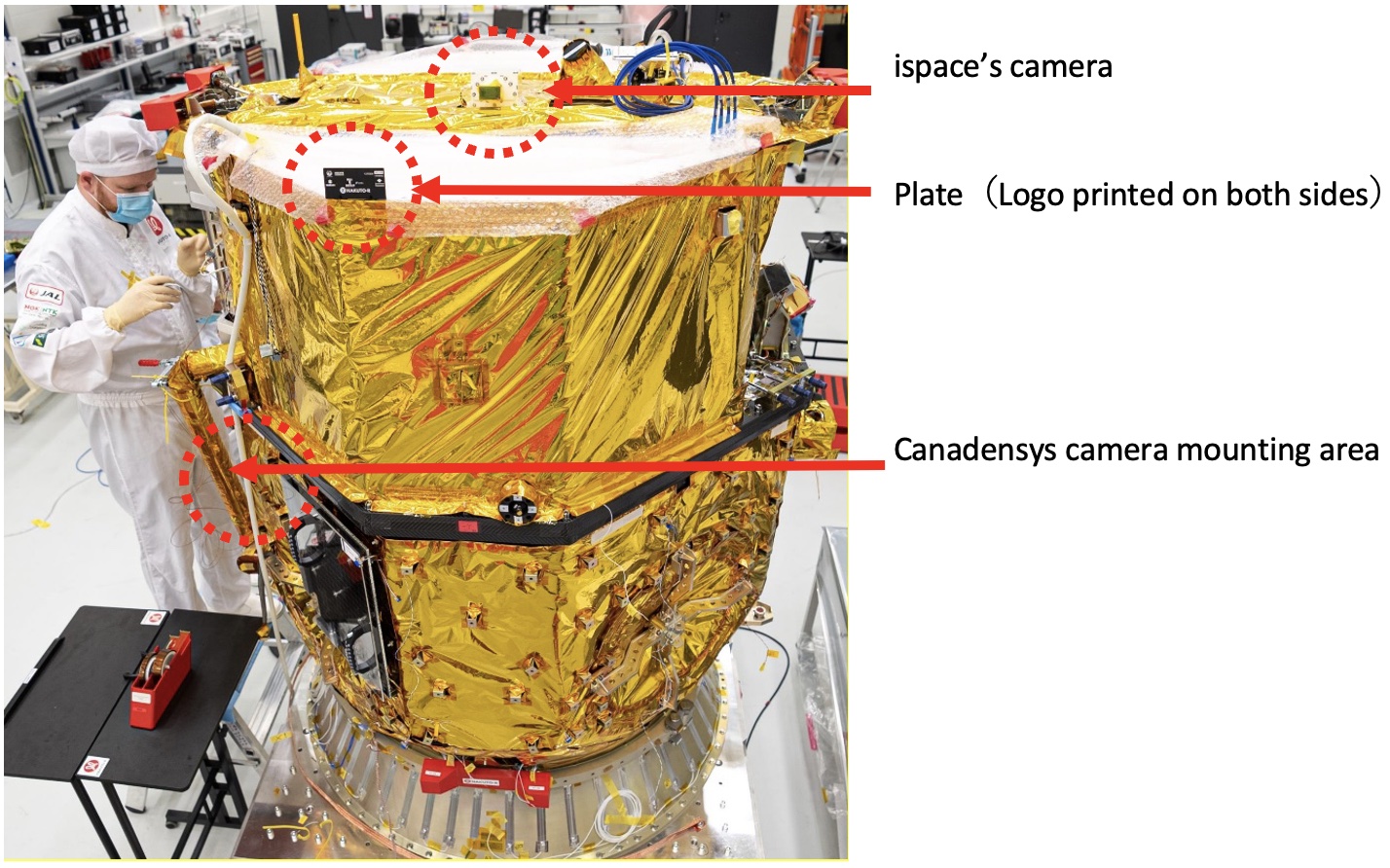
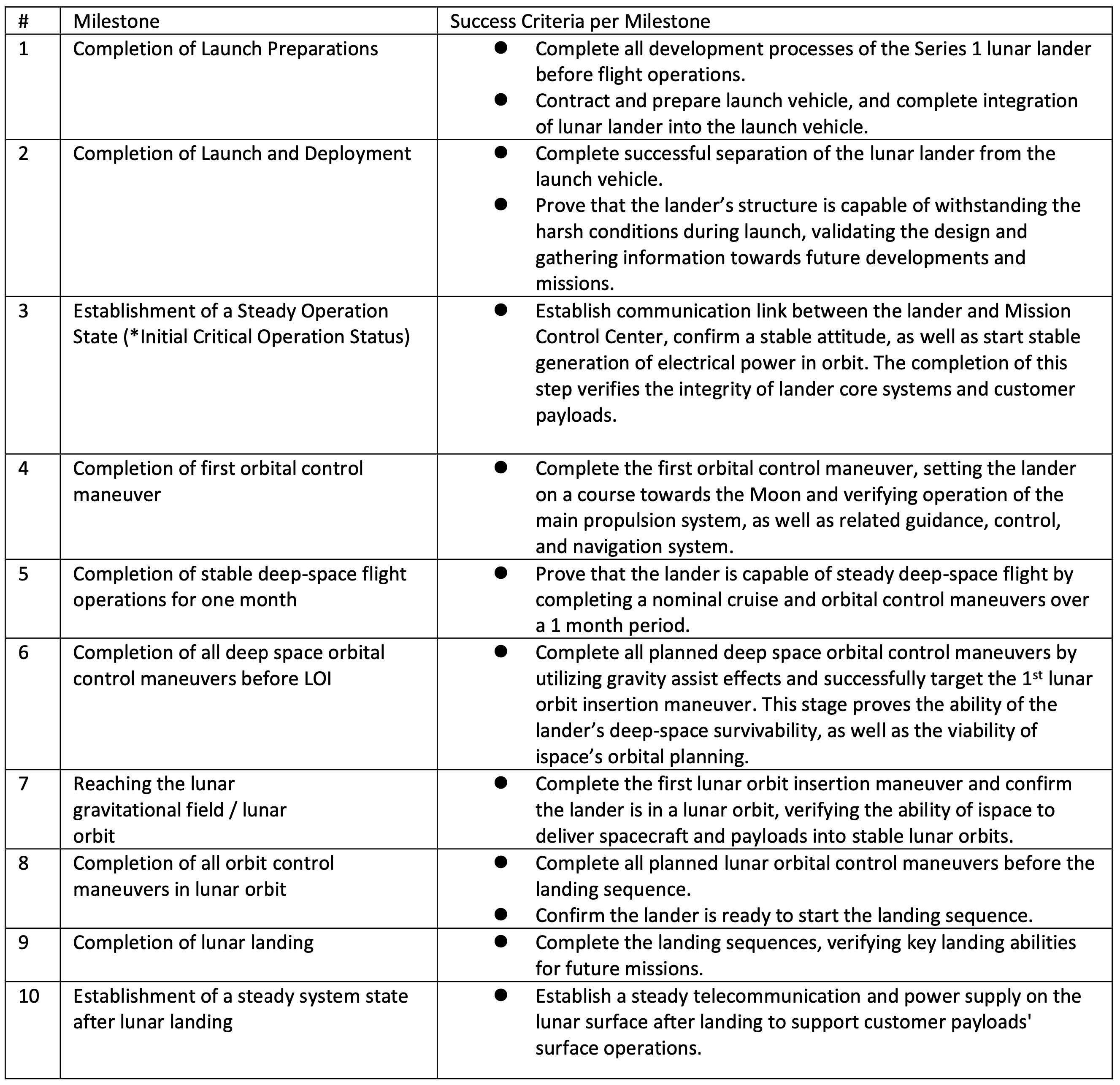
Mission 1 Milestones
For Mission 1, ispace has set 10 milestones between launch and landing, and aims to achieve the success criteria established for each of these milestones. Recognizing the possibility of an anomaly during the mission, the results will be weighed and evaluated against the criteria and incorporated into future missions already in development between now and 2025. Mission 2 and Mission 3, which also will contribute to NASA’s Artemis Program, will further improve the maturity of ispace’s technology and business model. Future announcements on progress of milestone achievement are expected to be released once attained.
About ispace, inc.
ispace, a global lunar resource development company with the vision, “Expand our Planet. Expand our Future.”, specializes in designing and building lunar landers and rovers. ispace aims to extend the sphere of human life into space and create a sustainable world by providing high-frequency, low-cost transportation services to the Moon. The company has offices in Japan, Luxembourg, and the United States with more than 200 employees worldwide. ispace technologies U.S., inc. is part of a team led by Draper, which was awarded a NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) Program contract to land on the far side of the Moon by 2025 (as of November 2022). Both ispace, and ispace EUROPE S.A. (ispace EU) were awarded contracts to collect and transfer ownership of lunar regolith to NASA, and ispace EU was selected by ESA to be part of the Science Team for PROSPECT, a program which seeks to extract water on the Moon.
Established in 2010, ispace operated “HAKUTO” which was one of five finalist teams in the Google Lunar XPRIZE race. The company’s first mission as part of its HAKUTO-R lunar exploration program launched on December 11, 2022, from the United States on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and is currently expected to land on the lunar surface around the end of April 2023. ispace has also launched a lunar data business concept to support new customers as a gateway to conduct business on the Moon.
For more information, visit: www.ispace-inc.com; Follow us on Twitter: @ispace_inc.